Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Usage of the ConjugateGradients class#
We illustrate the usage and available methods of the ConjugateGradients class via a small example.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.sparse import dia_matrix
import seaborn as sns
import EarlyStopping as es
np.random.seed(42)
sns.set_theme()
Generating synthetic data#
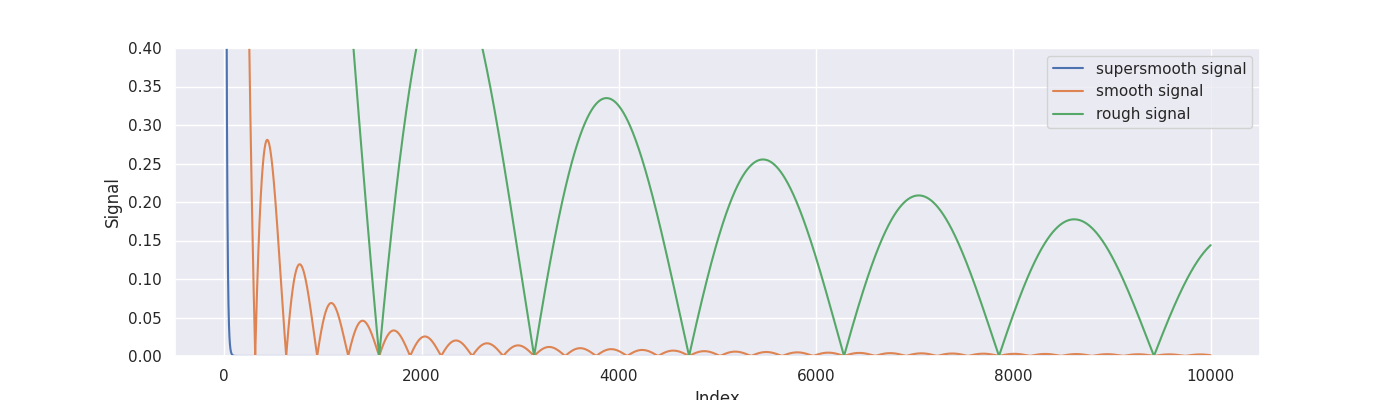
To simulate some data we consider the signals from Blanchard, Hoffmann and Reiß (2018).
sample_size = 10000
indices = np.arange(sample_size) + 1
signal_supersmooth = 5 * np.exp(-0.1 * indices)
signal_smooth = 5000 * np.abs(np.sin(0.01 * indices)) * indices ** (-1.6)
signal_rough = 250 * np.abs(np.sin(0.002 * indices)) * indices ** (-0.8)
true_signal = signal_rough
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 4))
plt.plot(indices, signal_supersmooth, label="supersmooth signal")
plt.plot(indices, signal_smooth, label="smooth signal")
plt.plot(indices, signal_rough, label="rough signal")
plt.ylabel("Signal")
plt.xlabel("Index")
plt.ylim([0, 0.4])
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
We simulate data from a prototypical inverse problem based on one of the signals.
true_noise_level = 0.01
noise = true_noise_level * np.random.normal(0, 1, sample_size)
eigenvalues = 1 / np.sqrt(indices)
design = dia_matrix(np.diag(eigenvalues))
response = eigenvalues * true_signal + noise
# Initialize ConjugateGradients class
alg = es.ConjugateGradients(
design,
response,
initial_value=None,
true_signal=true_signal,
true_noise_level=true_noise_level,
computation_threshold=10 ** (-8),
)
alg.iterate(sample_size)
UserWarning: No initial_value is given, using zero by default.
UserWarning: Algorithm terminates at iteration 128: norm of transformed residual vector (9.779623811691058e-09) <= computation_threshold (1e-08).
Empirical risk (weak/strong)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(indices[0 : alg.iteration + 1], alg.weak_empirical_risk, label="Weak empirical risk")
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
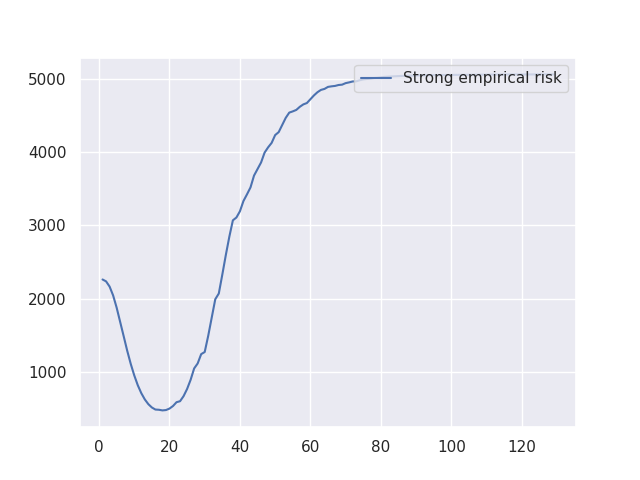
plt.plot(indices[0 : alg.iteration + 1], alg.strong_empirical_risk, label="Strong empirical risk")
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
print(f"Weak empirical oracle: {alg.get_weak_empirical_oracle(sample_size)}")
print(f"Strong empirical oracle: {alg.get_strong_empirical_oracle(sample_size)}")
UserWarning: Algorithm terminated due to computation_threshold before max_iteration. max_iteration is set to terminal iteration index.
Weak empirical oracle: 20
UserWarning: Algorithm terminated due to computation_threshold before max_iteration. max_iteration is set to terminal iteration index.
Strong empirical oracle: 17
Early stopping w/ discrepancy principle
critical_value = sample_size * true_noise_level**2
discrepancy_time = alg.get_discrepancy_stop(critical_value, sample_size)
estimated_signal = alg.get_estimate(discrepancy_time)
print(f"Critical value: {critical_value}.")
print(f"Discrepancy stopping time: {discrepancy_time}")
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 4))
plt.plot(indices, estimated_signal, label="Estimated signal at stopping time")
plt.plot(indices, true_signal, label="True signal")
plt.ylim([0, 2])
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
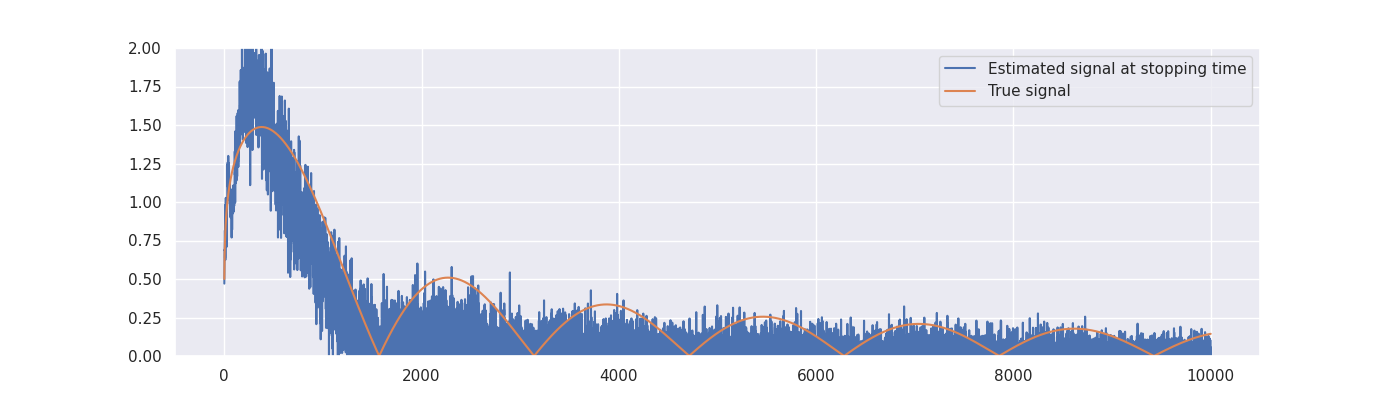
Critical value: 1.0.
Discrepancy stopping time: 15
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.810 seconds)